Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Provide a structure of the dipeptide Ala-Ser at biological pH.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following amino acids has its isoelectric point at the lowest pH?
A) arginine
B) aspartic acid
C) valine
D) glycine
E) methionine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nearly all naturally occurring amino acids:
A) are racemic mixtures.
B) are achiral.
C) have the (R) configuration at the α-carbon.
D) have the (S) configuration at the α-carbon.
E) have basic side chains.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Show the step-wise synthesis of glutamic acid starting with α-ketoglutarate and ammonia.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Provide a reasonable synthesis of racemic alanine from ethanol.
Correct Answer

verified
1. PCC
2. ...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
2. ...
View Answer
Essay
Show where chymotrypsin would cleave the peptide shown below. 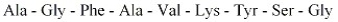
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Peptide bonds are:
A) ester linkages.
B) imido linkages.
C) ether linkages.
D) amide linkages.
E) disulfide linkages.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Draw the form of L-tryptophan which is present at biological pH.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following amino acids has its isoelectric point at the highest pH?
A) glycine
B) aspartic acid
C) valine
D) lysine
E) methionine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Provide the structure of L-arginine at pH 2.0.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
What compound is also known as Sanger reagent, and how is it used in peptide structure determination?
Correct Answer

verified
2,4-dinitrofluoroben...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Short Answer
Which type of protein, globular or fibrous, tends to function primarily as structural parts of an organism?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A protein bonded to a sugar residue would be classified as a:
A) simple protein.
B) glycoprotein.
C) lipoprotein.
D) metalloprotein.
E) nucleoprotein.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the practical limit on the use of carboxypeptidase in providing sequence information?
A) two residues on the C-terminal end
B) two residues on the N-terminal end
C) three residues on the N-terminal end
D) three residues on the C-terminal end
E) six residues on the N-terminal end
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The nonprotein part of a conjugated protein is called a ________ group.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following reagents is used to protect the amino group of the N-terminal residue in solution-phase peptide synthesis?
A) lithium diisopropyl amide
B) benzyl chloroformate
C) phenyl isothiocyanate
D) dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
E) trifluoroacetic acid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following amino acids has its isoelectric point at the highest pH?
A) glycine
B) aspartic acid
C) valine
D) arginine
E) methionine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The isoelectric point is important in:
A) the enzymatic resolution of amino acids.
B) electrophoresis.
C) determination of the C-terminal amino acid.
D) determination of the N-terminal amino acid.
E) the ninhydrin test.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the following pKa values, what is the major ionization state of histidine at pH 11? (α-COOH = 2.0, α-NH3+ = 9.0 and R-group imine = 6.5)
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 127
Related Exams