Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which reagent would be used for the following transformation? 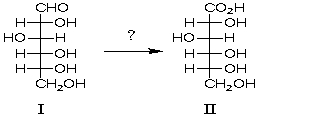
A) Ag(NH3) 2+
B) HNO3
C) Br2/H2O
D) HCl
E) Ag(NH3) 2+ and Br2/H2O
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
What products are expected from the reaction of 3-hydroxy-2,4-pentanedione with 2 molar equivalents of periodic acid?
Correct Answer

verified
11eaa4bc_3e41_38c2_9180_5b691e0078cd_TB5902_00
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sucrose reacts with which of these reagents?
A) C6H5NHNH2
B) Cu2+
C) Br2/H2O
D) H3O+
E) Ag(NH3) 2+
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many stereoisomers of the l series would exist for the following pentose? O=CHCHOHCHOHCHOHCH2OH
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 8
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A compound X reacts with 3 mol of HIO4 to yield 2 mol of HCO2H and 2 mol of HCHO.What is the structure of X? 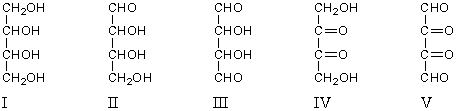
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these pyranose forms of an aldohexose can react with two equivalents of acetone in the presence of acid ? 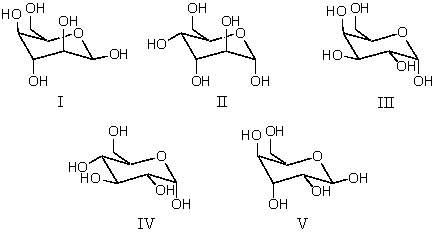
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a d-aldotetrose? 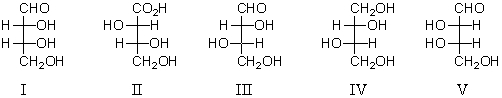
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Kiliani-Fischer synthesis is the reaction of an aldose with:
A) Br2/H2O; then HCN; then H3O+; then Na-Hg,H2O
B) HCN; then Ba(OH) 2; then H3O+; then Na-Hg,H2O
C) HCN; then H3O+; then Ba(OH) 2; then Na-Hg,H2O
D) Br2/H2O; then H2O2,Fe2(SO4) 3
E) Br2/H2O
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the structure of d-galacturonic acid? 
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reaction of the following substance with bromine water would yield: 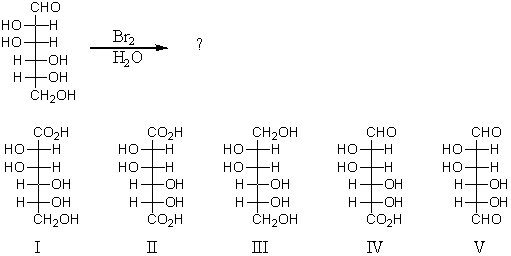
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The method of lengthening the carbon chain of an aldose through the addition of HCN followed by hydrolysis and reduction is called the ___.
Correct Answer

verified
Kiliani-Fi...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Which monosaccharide is recovered from the hydrolysis of starch?
A) d-Galactose
B) d-Gulose
C) d-Glucose
D) Cellobiose
E) Maltose
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these compounds,I,II,III,IV,is a reducing disaccharide? 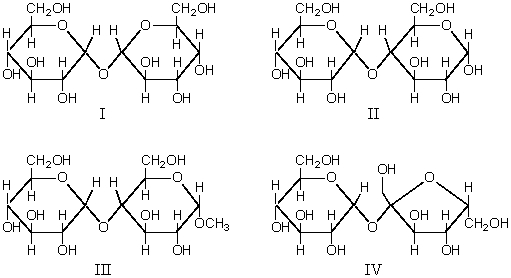
A) I alone
B) II alone
C) III alone
D) IV alone
E) I,II,III,and IV
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cellulose lacks nutritive value for humans because:
A) the products of its digestion are excreted without utilization.
B) its conformation prevents attack by digestive enzymes.
C) we lack the enzymes which can catalyze the hydrolysis of the glycosidic linkages.
D) it passes through the digestive tract so rapidly.
E) the molecules possess such a high molecular weight that enzymes can not hydrolyze it.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
When naturally occurring aldotetrose A is reduced with sodium borohydride,meso-1,2,3,4-butanetetrol is formed.What are the name and structure of A?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the ratio of products formed by the reaction of periodic acid with the following compound? 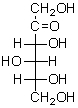 H2C=O HCO2H CO2 I 5 1 0
II 3 3 0
III 1 5 0
IV 2 3 1
V 0 4 2
H2C=O HCO2H CO2 I 5 1 0
II 3 3 0
III 1 5 0
IV 2 3 1
V 0 4 2
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reaction of the following substance with sodium borohydride (NaBH4) would yield: 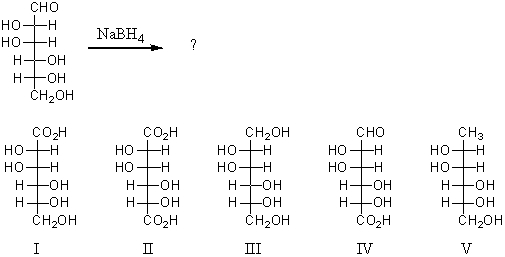
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are carbohydrates? 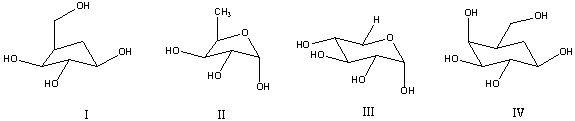
A) I,II,III
B) I,II
C) II,III
D) I,II,III,IV
E) III,IV
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
What are the names of the following structures? 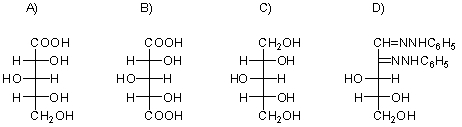
Correct Answer

verified
a)d-xylonic acid
b)d-xylaric acid
c)d-xylitol
d)d-xylose phenylosazone
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 124
Related Exams