A) A = G
B) A + G = C + T
C) A + T = G + C
D) A = C
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the function of the enzyme topoisomerase in DNA replication?
A) relieving strain in the DNA ahead of the replication fork caused by the untwisting of the double helix
B) elongating new DNA at a replication fork by adding nucleotides to the existing chain
C) reattaching the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs in the double helix
D) building RNA primers using the parental DNA strand as a template
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose you are provided with an actively dividing culture of E. coli bacteria to which radioactive thymine has been added. What would happen if a cell replicates once in the presence of this radioactive base?
A) One of the daughter cells, but not the other, would have radioactive DNA.
B) Neither of the two daughter cells would be radioactive.
C) All four bases of the DNA would be radioactive.
D) DNA in both daughter cells would be radioactive.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements accurately describes the differences between DNA replication in prokaryotes and DNA replication in eukaryotes?
A) Prokaryotic chromosomes have histones, whereas eukaryotic chromosomes do not.
B) Prokaryotic chromosomes have a single origin of replication, whereas eukaryotic chromosomes have many.
C) The rate of elongation during DNA replication is slower in prokaryotes than in eukaryotes.
D) Prokaryotes produce Okazaki fragments during DNA replication, but eukaryotes do not.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure to answer the following question.
Single strand as a template plus end to start DNA synthesis
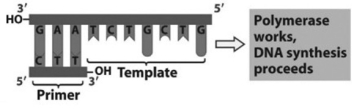 Referring to the figure, what bases will be added to the primer as DNA replication proceeds?
Referring to the figure, what bases will be added to the primer as DNA replication proceeds?
A) 5? C, A, G, C, A, G, A 3?
B) 3? T, C, T, G, C, T, G 5?
C) 5? A, G, A, C, G, A, C 3?
D) 3? G, T, C, G, T, C, T 5?
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In DNA replication, the resulting daughter molecules contain one strand of the original parental DNA and one new strand. What is the explanation for this phenomenon?
A) DNA replication is semiconservative.
B) DNA replication is conservative.
C) DNA replication is not conservative.
D) RNA synthesis is conservative.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who performed classic experiments that supported the semiconservative model of DNA replication?
A) Watson and Crick
B) Meselson and Stahl
C) Hershey and Chase
D) Franklin and Wilkins
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is meant by the description "antiparallel" regarding the two strands that make up the DNA double helix?
A) The double helix structure of DNA creates nonparallel strands.
B) The 5' to 3' direction of one strand runs counter to the 5' to 3' direction of the other strand.
C) Base pairings create unequal spacing between the two DNA strands.
D) One strand contains only purines and the other contains only pyrimidines.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the role of DNA ligase in the elongation of the lagging strand during DNA replication?
A) It synthesizes RNA nucleotides to make a primer.
B) It joins Okazaki fragments together.
C) It unwinds the parental double helix.
D) It stabilizes the unwound parental DNA.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the enzyme telomerase meet the challenge of replicating the ends of linear chromosomes?
A) It adds a single 5' cap structure that resists degradation by nucleases.
B) It causes specific double-strand DNA breaks that result in blunt ends on both strands.
C) It catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres, compensating for the shortening that could occur during replication without telomerase activity.
D) It adds numerous GC pairs, which resist hydrolysis and maintain chromosome integrity.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After the first replication was observed in their experiments testing the nature of DNA replication, Meselson and Stahl could be confident of which of the following conclusions?
A) Replication is semi-conservative.
B) Replication is not dispersive.
C) Replication is not conservative.
D) Replication is neither dispersive nor conservative.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The elongation of the leading strand during DNA synthesis
A) progresses away from the replication fork.
B) occurs in the 3′ → 5′ direction.
C) produces Okazaki fragments.
D) depends on the action of DNA polymerase.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A biochemist isolates, purifies, and combines in a test tube a variety of molecules needed for DNA replication. When she adds some DNA to the mixture, replication occurs, but each DNA molecule consists of a normal strand paired with numerous segments of DNA a few hundred nucleotides long. What has she probably left out of the mixture?
A) DNA polymerase
B) DNA ligase
C) Okazaki fragments
D) primase
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes the process of transformation in bacteria?
A) A strand of DNA is created from an RNA molecule.
B) A strand of RNA is created from a DNA molecule.
C) Bacterial cells are infected by a phage DNA molecule.
D) External DNA is taken into a cell, becoming part of the cell's genome.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following facts did Hershey and Chase make use of in trying to determine whether DNA or protein is the genetic material?
A) DNA contains sulfur, whereas protein does not.
B) DNA contains phosphorus, whereas protein does not.
C) DNA contains nitrogen, whereas protein does not.
D) DNA contains purines, whereas protein includes pyrimidines.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a cell were unable to produce histone proteins, which of the following results would be a likely effect on the cell?
A) There would be an increase in the amount of DNA produced during replication.
B) The cell's DNA could not be packed into its nucleus.
C) Spindle fibers would not form during prophase.
D) Amplification of other genes would compensate for the lack of histones.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an analysis of the nucleotide composition of a molecule of DNA, which of the following combinations of base pairs will be found?
A) A = C
B) A = G and C = T
C) A + C = G + T
D) G + C = T + A
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hershey and Chase set out to determine what molecule served as the unit of inheritance. They completed a series of experiments in which E. coli was infected by a T2 virus. Which molecular component of the T2 virus actually ended up inside the cell?
A) protein
B) RNA
C) ribosome
D) DNA
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At a specific area of a chromosome, the sequence of nucleotides below is present where the chain opens to form a replication fork: 3' C C T A G G C T G C A A T C C 5' An RNA primer is formed starting at the underlined T (T) of the template. Which of the following represents the primer sequence?
A) 5' G C C T A G G 3'
B) 5' A C G T T A G G 3'
C) 5' A C G U U A G G 3'
D) 5' G C C U A G G 3'
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Individuals with the disorder xeroderma pigmentosum are hypersensitive to sunlight, and mutations to the DNA in their skin cells are left uncorrected. Why are the mutations not corrected in individuals with this disorder?
A) The disorder makes cells unable to replicate DNA.
B) The disorder causes mitosis to stop during metaphase.
C) The disorder makes cells unable to form chromosomes.
D) The disorder causes cells to be unable to repair thymine dimers.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 65
Related Exams