A) local infections.
B) bacteremia.
C) systemic infections.
D) sepsis.
E) septicemia.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A needlestick is an example of
A) indirect contact transmission by fomite.
B) direct contact.
C) droplet transmission.
D) direct biological transmission by vector.
E) vehicle transmission.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Koch observed Bacillus anthracis multiplying in the blood of cattle. What is this condition called?
A) bacteremia
B) systemic infection
C) focal infection
D) local infection
E) septicemia
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is NOT a zoonosis?
A) Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome
B) tapeworm
C) rabies
D) cat-scratch disease
E) All of these are zoonoses.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Both normal and transient flora can become opportunistic pathogens.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rise in herd immunity amongst a population can be directly attributed to
A) vaccinations.
B) improved handwashing.
C) increased use of antibiotics.
D) antibiotic-resistant microorganisms.
E) None of the answers is correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pseudomonas bacteria colonized the bile duct of a patient following his liver transplant surgery. This is an example of a
A) nosocomial infection.
B) communicable disease.
C) sporadic disease.
D) latent infection.
E) None of the answers is correct.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A researcher has performed a prospective study on a disease. To which specific kind of epidemiological study is this referring?
A) analytical
B) prodromal
C) case control
D) experimental
E) descriptive
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Symptoms of disease differ from signs of disease in that symptoms
A) are changes felt by the patient.
B) are specific for a particular disease.
C) always occur as part of a syndrome.
D) are changes observed by the physician.
E) None of the answers is correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about biological transmission is FALSE?
A) The pathogen may enter the host in the vectorʹs feces.
B) Houseflies are an important vector.
C) The pathogen may be injected by the bite of the vector.
D) The pathogen may require the vector as a host.
E) The pathogen reproduces in the vector.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A host is not considered diseased until an infection changes oneʹs state of health.)
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) At least one member must benefit in a symbiotic relationship.
B) Members of a symbiotic relationship cannot live without each other.
C) Symbiosis always refers to different organisms living together and benefiting from each other.
D) A parasite is not in symbiosis with its host.
E) Both members are harmed in a symbiotic relationship.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT an example of microbial antagonism?
A) acid production by bacteria
B) bacteria causing disease
C) bacteriocin production
D) bacteria occupying host receptors
E) bacteria producing vitamin K
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 14.2 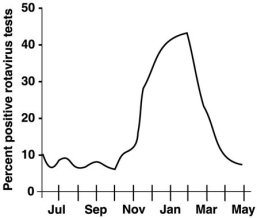 In Figure 14.2, when is the prevalence the highest?
In Figure 14.2, when is the prevalence the highest?
A) February
B) January
C) July
D) March
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The yeast Candida albicans does not normally cause disease because of
A) antagonistic bacteria.
B) other fungi.
C) commensal bacteria.
D) symbiotic bacteria.
E) parasitic bacteria.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The major significance of Robert Kochʹs work is that
A) microorganisms can be cultured.
B) microorganisms cause disease.
C) microorganisms are present in a diseased animal.
D) diseases can be transmitted from one animal to another.
E) microorganisms are the result of disease.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a fomite?
A) a hypodermic needle
B) insects
C) water
D) pus
E) droplets from a sneeze
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a predisposing factor of disease?
A) genetic background
B) occupation
C) lifestyle
D) climate
E) All of these are predisposing factors of disease.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Reservoirs of infections are always animate objects.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Transient microbiota differ from normal microbiota in that transient microbiota
A) are always acquired by direct contact.
B) never cause disease.
C) are found in a certain location on the host.
D) are present for a relatively short time.
E) cause diseases.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 51
Related Exams