Which of the following measures of central tendency is not appropriate when you have extreme scores in your sample data?
A) Mode
B) Median
C) Mean
D) None of the above
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Questions relate to the following histogram:
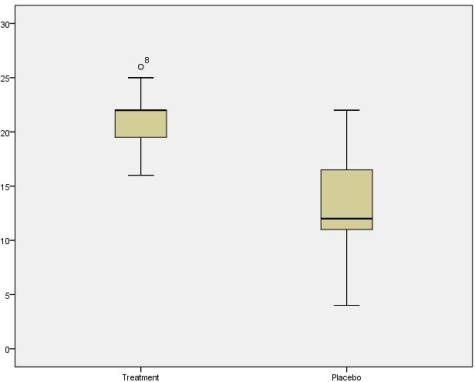 -What is the median for the Placebo group?
-What is the median for the Placebo group?
A) 4
B) 17
C) 12
D) 22
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified