A) kills all microorganisms.
B) may result in the survival of thermophiles.
C) may result in the survival of fungal spores.
D) kills only bacteria.
E) employs a higher temperature.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are growing Bacillus subtilis, an aerobic bacterium that can also carry out fermentation when required, in a bioreactor and notice that the growth rate has slowed and the pH has decreased. You suspect the bacteria are
A) fermenting.
B) using proteins.
C) photosynthesizing.
D) using the Krebs cycle.
E) dead.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Mesophilic bacteria grow best at temperatures of 60°C.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Biomass is a renewable energy source derived from the organic matter produced by living organisms. All of the following are sources of biomass EXCEPT
A) algae.
B) oxidation of metals.
C) crops.
D) landfill sites.
E) bacteria.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The longer interior-ripened cheeses are permitted to ripen, the milder the taste of the cheese.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are advantages of a bioreactor instead of a flask culture EXCEPT
A) instrumentation for monitoring environmental conditions.
B) uniform aeration and mixing.
C) larger culture volumes can be grown.
D) aseptic sampling.
E) None of the answers is correct; all of these are advantages of using a bioreactor instead of a flask culture.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 28.1
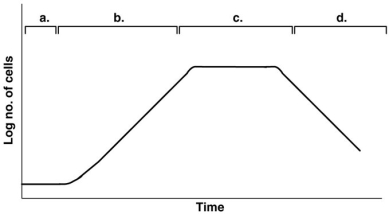 -In Figure 28.1, assume the cells are producing penicillin which is collected during the idiophase. Remember, the top lines/markings indicate the different phases observed in the curve below them. When would you be able to collect the penicillin?
-In Figure 28.1, assume the cells are producing penicillin which is collected during the idiophase. Remember, the top lines/markings indicate the different phases observed in the curve below them. When would you be able to collect the penicillin?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is used for the recovery of from ore.
A) gold
B) sulfur
C) sulfuric acid
D) iron
E) copper
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are industrial products produced using microbial fermentations EXCEPT
A) riboflavin.
B) citric acid.
C) glutamic acid.
D) aspartic acid.
E) saccharin.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are industrial products produced by microbes EXCEPT
A) vitamin B12 and riboflavin.
B) industrial enzymes.
C) amino acids in food supplements.
D) uranium.
E) antibiotics.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following reactions makes wine less acidic, and is important for good flavor when grapes with higher acidity are used?
A) carbon dioxide → sucrose
B) ethanol → acetic acid
C) sugar → Co2 + H2O
D) sugar → ethanol
E) malic acid → lactic acid
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are true of irradiation methods used for food preservation and sterilization EXCEPT
A) they prolong shelf-life of fruits and vegetables.
B) they are used for the sterilization of many spices.
C) they greatly reduce the number of pathogens present in meats and poultry.
D) residual radioactivity is left behind on many foods.
E) ionizing radiation such as X rays or gamma rays is used.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aseptic packaging utilizes which of the following to sterilize laminated paper or plastic prior to filling with food?
A) hot hydrogen peroxide solution
B) hot HCl solution
C) autoclave
D) X rays
E) gamma radiation
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following steps are required for making cheese. What is the second step, which helps to provide the characteristic flavors and aromas of the cheese?
A) enzymatic coagulation of milk
B) separation of curds and whey
C) inoculation with lactic acid bacteria
D) inoculation with Penicillium
E) fermentation of curd
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Microbial products can be improved by all of the following EXCEPT
A) isolating new strains.
B) mutating existing strains.
C) sterilization.
D) genetically modifying strains.
E) modifying culture conditions.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Canning preserves food
A) by exposure to radiation.
B) by exposure to high pH.
C) by exposure to chemicals.
D) through use of aseptic packaging.
E) by exposure to high heat.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 28.1
 -In Figure 28.1, assume that a secondary metabolite is your desired product. Remember, the top lines/markings indicate the different phases observed in the curve below them. When would you be able to obtain it?
-In Figure 28.1, assume that a secondary metabolite is your desired product. Remember, the top lines/markings indicate the different phases observed in the curve below them. When would you be able to obtain it?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following microorganisms is usually used in the fermentation of alcoholic beverages?
A) Lactobacillus
B) Saccharomyces
C) Propionobacterium
D) Rhizopus
E) Penicillium
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Canning works to preserve foods through
A) increasing pH.
B) creation of an anaerobic environment.
C) exposure to high heat.
D) mutation of bacterial DNA.
E) creation of an anaerobic environment and exposure to high heat.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The blue-green clumps observed in Roquefort cheese are a result of mold growth.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 59
Related Exams