A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the name of the following compound? 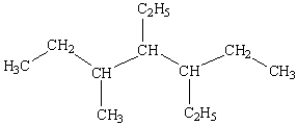
A) 3,4-diethyl-5-methylheptane
B) 3,4,5-heptane
C) 3-ethyl-5-(2-butyl) hexane
D) 3-(2-butyl) -3-ethylhexane
E) 3,5,6-trimethylheptane
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following alkenes is capable of forming cis-trans isomers?
A) (CH3) 2 = CH2
B) (CH3) 2 = CHBr
C) CH3CH = CH2
D) CH3CH = CBr2
E) CHBr = CHD
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following acids is found in grapes?
A) Tartaric acid
B) Acetic acid
C) Caproic acid
D) Uric acid
E) Oxalic acid
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following class of compounds is responsible for many of the distinctive odors of artificial flavors and perfumes?
A) Ethers
B) Aldehydes
C) Esters
D) Amides
E) Alkenes
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the structures below has the common name p-dichlorobenzene (where p- is para) ?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The addition of Br2 is used as the reaction to distinguish between alkanes and alkenes.What is the observation that accompanies this test?
A) A bright red color is produced when Br2 reacts with an alkene.
B) Bromine dissolves in alkanes but not in alkenes.
C) Bromine is a dark red liquid.When it adds to the double bond of an alkene to make the dibromide,it becomes colorless.
D) The red color of bromine disappears when it dissolves in alkanes.
E) Bromine reacts with alkanes to form a precipitate.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction of methane with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet radiation can produce ____.
A) chloromethane
B) dichloromethane
C) trichloromethane
D) carbon tetrachloride
E) all of these products
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mixture of ethanol and benzoic acid is heated in the presence of an acid.Which of the following is the primary product of this reaction?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of compounds must have an sp2-hybridized carbon center?
A) esters
B) ethers
C) cycloynes
D) amines
E) alcohols
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction of 1-propanol with K2Cr2O7 in acidic solution to produce propanal is what kind of reaction?
A) polymerization
B) combustion
C) oxidation
D) reduction
E) double displacement
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the name of the following benzene derivative? 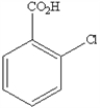
A) 1-chlorobenzoic acid
B) 5-chloroanaline
C) 1-acetate-1-chlorobenzene
D) 5-chlorobenzoic acid
E) 1,3-chlorocarboxylic benzene
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following formulas represents an unsaturated hydrocarbon?
A) C2H6
B) C3H8
C) C4H10
D) C6H12
E) C7H16
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following chemical equations depicts a halogenation reaction with benzene?
A) C6H6( ![]() ) + 3 Br2(g) → 3 C2H2Br2(g)
) + 3 Br2(g) → 3 C2H2Br2(g)
B) C6H6( ![]() ) + Cl2(g) → C6H5Cl(
) + Cl2(g) → C6H5Cl( ![]() ) + HCl(g)
) + HCl(g)
C) C6H6( ![]() ) + CH3I(g) → C6H5CH3(
) + CH3I(g) → C6H5CH3( ![]() ) + HI(g)
) + HI(g)
D) C6H6( ![]() ) + Cl2(g) → C6H4Cl2(
) + Cl2(g) → C6H4Cl2( ![]() ) + H2(g)
) + H2(g)
E) C6H6( ![]() ) + 3 Br2(g) → 6 C6H6Br6(g)
) + 3 Br2(g) → 6 C6H6Br6(g)
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a secondary alcohol is oxidized,the product is a(n) ____.
A) ketone
B) ether
C) ester
D) aldehyde
E) amide
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an aldehyde is oxidized,the product is a(n) ____.
A) ester
B) ketone
C) ether
D) alcohol
E) carboxylic acid
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Four of the following compounds are structural isomers.Which one is not?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the name of the given molecule? 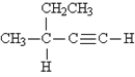
A) 1-hexyne
B) 2-ethynyl butane
C) 2-ethyl-3-butyne
D) 3-methyl-1-pentyne
E) 3-methyl-4-pentyne
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the balanced chemical equation for the combustion of 4-methyl-1-pentene?
A) 2 C5H10(g) + 15 O2(g) → 10 CO2(g) + 10 H2O( ![]() )
)
B) 2 C4H10(g) + 13 O2(g) → 8 CO2(g) + 10 H2O( ![]() )
)
C) C4H8(g) + 6 O2(g) → 4 CO2(g) + 4 H2O( ![]() )
)
D) C6H12(g) + 9 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O( ![]() )
)
E) C5H12(g) + 13 O2(g) → 5 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O( ![]() )
)
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the name of the following compound? 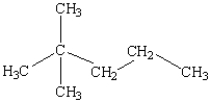
A) 1,1,1-trimethylbutane
B) 3-butylpropane
C) 2-methyl-2-propylpropane
D) 4,4-dimethylpentane
E) 2,2-dimethylpentane
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 88
Related Exams